Lithium batteries power many devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Safety is a top priority due to occasional incidents like explosions. Understanding battery safety is crucial.
This article explores the safety of lithium batteries, highlighting risks and safety measures. Stay informed to use lithium batteries safely.
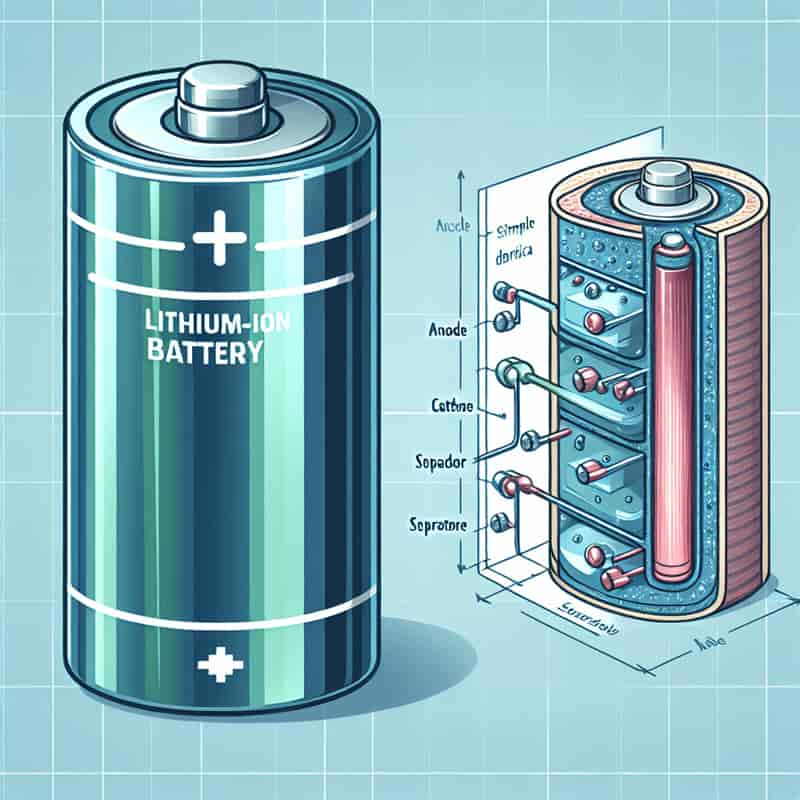
What is a lithium battery?
Lithium batteries, like lithium-ion batteries, are rechargeable batteries found in phones, laptops, and power banks. They store energy by moving lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging cycles.
These batteries are popular for their high power and energy density, providing long-lasting power in small sizes. However, it’s important to know that lithium batteries can be dangerous, with risks of fire and explosion if not handled correctly. Safe storage, charging, and maintenance are necessary to reduce these risks.
Application of lithium battery
Lithium batteries are widely used in phones, laptops, and power banks because they have high energy density and fast-charging capabilities.
Using lithium batteries in these devices improves efficiency and sustainability by reducing overall energy consumption in daily activities.
Factors like proper charge management, safety during charging, and avoiding over-discharge help prolong the lifespan of lithium batteries in various applications.
How does lithium battery work
Lithium-ion batteries store energy by moving lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes when charging and discharging.
Components of a lithium-ion cell are a positive electrode made of lithium manganese oxide or lithium cobalt oxide, a negative electrode of graphite, and an electrolyte that helps ion movement.
The lifespan of lithium batteries is influenced by usage, charging routines, and environmental factors. Typically, after 500 charge cycles, most lithium-ion batteries keep about 80% of their original capacity.
Importance of Lithium battery
Lithium batteries power many devices like phones and laptops. They charge quickly, which is great for daily use. These batteries work by moving lithium ions between the positive and negative parts while charging and discharging. A lithium-ion cell has a cathode, anode, and electrolyte. The cathode is lithium metal oxide, the anode is often graphite, and the electrolyte is liquid or gel with lithium salt. These parts help move lithium ions for energy storage.
Lithium battery life
The lifespan of a lithium-ion battery, in terms of charge/discharge cycles, varies depending on the type and usage. Most lithium-ion batteries can sustain around 300 to 500 charge/discharge cycles before their capacity significantly degrades . Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, a specific type of lithium-ion battery, can undergo thousands of cycles due to their higher stability and longevity . Manufacturers typically expect a minimum lifespan of 5 years or at least 2,000 charging cycles for lithium-ion batteries under ideal conditions .
Are lithium batteries safe
Despite their convenience, these batteries can be risky. They may catch fire if they get too hot, are damaged, or not charged correctly.
To stay safe with lithium batteries:
Avoid overcharging.
Store them properly to avoid short circuits.
Use good chargers to lower the risk of accidents.
Compared to lithium polymer batteries, lithium batteries store more energy but can be more dangerous if mishandled.
How do lithium-ion batteries store energy
Lithium-ion batteries store energy by moving lithium ions between electrodes during charging and discharging. These batteries have an anode (made of graphite), a cathode (made of lithium metal oxide), and an electrolyte (a solution with lithium ions). A separator prevents short circuits, and a casing offers protection. When charging, lithium ions go to the anode, and during discharge, they go back.
What are the components of a lithium-ion cell?
A lithium-ion cell has several components:
- Cathode
- Anode
- Separator
- Electrolyte
- Collector
The cathode is made of lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, or lithium iron phosphate. The anode is typically graphite.
The separator, a porous polymer film, keeps the cathode and anode apart while enabling lithium ion flow. The electrolyte, a lithium salt in a solvent, helps lithium ions move between the cathode and anode.
The collector, often aluminum for the cathode and copper for the anode, acts as the current collector. Each component has a specific role in the cell’s operation.
The cathode and anode store and release lithium ions. The electrolyte aids in lithium ion transfer, and the separator prevents short circuits. The collector allows electron flow, completing the circuit.
Lithium battery types
There are several types of lithium batteries, each with unique characteristics suitable for various applications. The six main types based on electrode materials include:
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC): Offers a good balance between power capacity, lifespan, and safety.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): Known for its long life and safety, but has a lower energy density.
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO): Provides high energy density but has safety risks.
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA): Similar to NMC, offering high energy density and safety.
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO): Offers high power output and thermal stability, with a moderate energy density.
- Lithium Titanate (LTO): Stands out for its fast recharge capability and excellent safety, though at the cost of lower energy density .
Additionally, there are lithium batteries differentiated by form, such as:
- Aqueous lithium-ion battery
- Lithium-ion flow battery
- Lithium ion manganese oxide battery
- Lithium polymer battery
- Lithium–silicon battery
- Lithium-titanate battery .
These types cater to a wide range of applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems.
FAQ
How do I know if I have a lithium battery?
Lithium batteries have specific markings like “Li-ion” or “LiPo” on the label.
Lithium battery vs alkaline
Lithium-ion batteries and alkaline batteries are different.
Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density and longer lifespan. They are great for high-power devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. On the other hand, alkaline batteries are better for low-power devices such as remote controls or wall clocks due to their lower energy density.
Lithium batteries excel in fast-charging and capacity retention over multiple charge cycles, unlike alkaline batteries.
Alkaline batteries have a more stable chemical composition and are less likely to undergo thermal runaway. Despite this, lithium batteries offer a more efficient and reliable power source for high-demand applications.
Lithium-ion battery vs lead-acid battery
Lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries have differences.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for:
- High power density
- Fast charging capabilities
- Longer lifespan
They may cost more initially, but their total costs over time are often lower due to efficiency and durability.
Lithium-ion batteries are also more eco-friendly:
- Do not contain harmful materials like lead and sulfuric acid
- Reduce the risk of soil and water contamination
- Easier to recycle with less waste
Using lithium-ion batteries is safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly compared to lead-acid batteries in different applications.
What’s the difference between a lithium battery and a regular battery?
Lithium-ion batteries and regular batteries have some differences. Lithium batteries have higher energy density, which means devices can charge faster and last longer. They also have a lower self-discharge rate, making them great for long-term use in power banks.
Additionally, lithium batteries have higher power density, allowing devices to work well even with high power needs.
